「金銭的な価値のあるもの|一発理解!相続税の謎解き!」
〜前回のつづき〜
●相続=相続税ではない!~本当にかかる金額、知っていますか?~(つづき)

ではこの一定金額とは
どれぐらいの金額なのか?
基礎控除で3000万円
+
法定相続人の数×600万円
例えば
息子一人で全部相続するんだ
という事であれば
3000+600=3600万円
ここまでは税金が掛からない。
子供二人で相続するとなると
3000+600×2=4200万円
までは税金が掛からない。
そして配偶者(夫or妻)には
配偶者控除というのがあるので
遺産総額が1億6千万円までは
かからないんですよ。
なので相続税が掛かる人は
一部だけなんです。
ザックリ覚えておけばOKです。
このぐらいは掛からないんだ
というのが頭の中にあるだけでも
全然違うと思います。
●基礎控除を超えた分だけ、相続税はステップアップ!

基礎控除を超えたらどうなるのか?
これは確かに
相続税がかかるんですけど
基礎控除を超えてしまった場合
基礎控除額を超えた分だけ
かかるんです。
例えば
子供一人で相続するとして
基礎控除が3600万円有ったとする。
4600万円の財産を相続すると
4600-3600=1000万円
この1000万円に対して
相続税がかかるんですね。
(出典:https://souzoku.asahi.com/article/14937828)
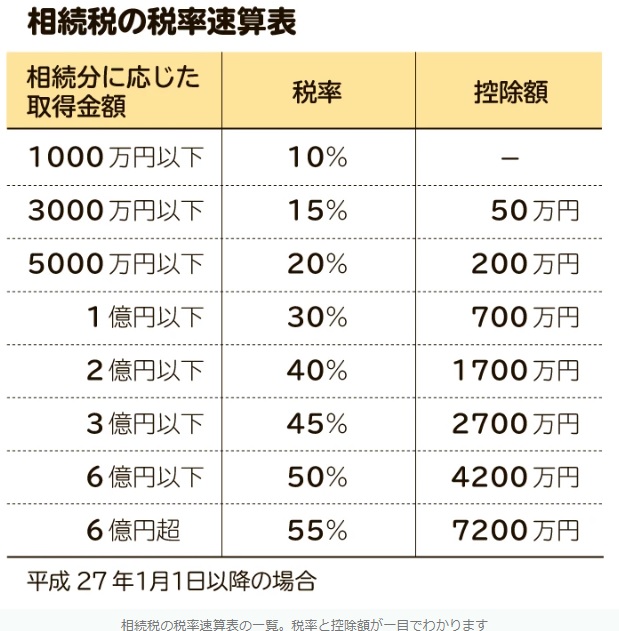
基礎控除を超えたのは1000万円なので
相続税は10%かかるという事です。
よくある勘違いなんですけど
1100万円相続してしまった場合は
3000万円以下のゾーンの
15%の税金がかかるのかと
思うかもしれませんが
そうではありません。
1100万円相続したとしても
1000万円以下の分は10%
1000×10%=100万円
1000万円を超えた
100万円の部分だけ15%
100×15%=15万円
それぞれかかるようになっています。
これは所得税と一緒なので
覚えておいて下さい。
●相続税はあなたの財産すべてに関わる!

相続税はどんな財産にかかるのか?
そもそも
税金を計算する場合の財産とは
何なのか?
- 現金
- 口座の預金
- 車
- 不動産
- 貴金属
など色々あります。
その他
金銭的な価値のあるもの全てです。
みなし相続財産
というのも有って
生命保険も財産として
みなされるという事です。
ただし生命保険金の場合は
500万円×法定相続人の数
が非課税だという事もあり
全額かかってくるわけではないんですけど
全額財産になるという訳ではありません。
あとは
国外資産も税金はかかってきます。
財産とみなされます。
例外もありますが
基本的にはかかってきます。
財産としてみなされる
という事です。
あとは名義預金ですね。
他人名義の
実質自分の預金などですね。
例えば
子供にいつかあげるために
子供の名義で作っておいて
ちょっとずつ貯金しておいた
口座預金などです。
実質相続税対策であったとしても
そういったものにもかかってくるので
注意して下さい。
〜〜〜つづく〜〜〜
Special Thanks college president Ryo.

●おまけ
≪≪Chat-GPTくんによる要約→perplexityちゃんによる文章まとめ≫≫
相続税は、多くの人が誤解している部分があります。まず、相続税がかかる金額について知っておくことが重要です。基礎控除は3,000万円から始まり、法定相続人1人につき600万円が加算されます。例えば、息子一人で相続する場合には3,600万円までは税金がかかりません。子供二人であれば4,200万円まで非課税です。また、配偶者には特別な控除があり、遺産総額が1億6千万円までは課税されません。
基礎控除を超えた部分にのみ相続税がかかります。この場合も累進課税方式で計算されます。例えば、4,600万円の財産を子供一人で相続した場合、そのうち1,000万円(4,600 – 3,600)に対して10%の相続税がかかります。
また、どのような財産にも課税される可能性があります。これには現金や預金だけでなく車や不動産なども含まれます。また生命保険の保険金も一定条件下でみなし財産として扱われ、一部は非課税ですが全額ではないことも注意点です。他にも国外資産や名義預金(実質的に自分のものとされるもの)も対象となり得るため、これらについても十分な注意が必要です。
このようにして理解することで、「これだけは掛からない」というイメージを持つだけで大きな違いが出てきてしまいます。そのため、これらのポイントをしっかりと把握し、それに応じた計画を行うことが大切です。
Citations:
[1] https://www.resonabank.co.jp/kojin/column/shoukei/column_0013.html
[2] https://chester-tax.com/encyclopedia/8749.html
[3] https://souzoku-yokohama.net/inheritance-tax/4734/
[4] https://www.zeirisi.co.jp/souzokuzei-keisan/inheritance-tax-basic-deduction/
[5] https://www.smtb.jp/personal/entrustment/entrustment-column/column-08
[6] https://legacy.ne.jp/knowledge/now/souzoku-zei/149-ikurakakaru-3600manen-meyasu/
[7] https://www.nta.go.jp/taxes/shiraberu/taxanswer/sozoku/4155.htm
[8] https://www.orixbank.co.jp/column/article/188/
[9] https://fuji-sogo.com/sozoku_knowledge/how_much_inheritance_tax/
≪≪Chat-GPTくんによる英訳≫≫
~Continuation from the previous section~
【Inheritance ≠ Inheritance Tax! – Do You Really Know the Amount that Will Be Taxed? (Continued)】
So, what exactly is this certain amount?
The basic deduction is 30 million yen
+
600,000 yen × the number of legal heirs
For example, if one son inherits everything,
the total is 3,000,000 + 600,000 = 3,600,000 yen,
and no tax is applied up to this amount.
If two children inherit,
then 3,000,000 + (600,000 × 2) = 4,200,000 yen,
and no tax is applied up to this amount.
Also, spouses (husband or wife) are eligible for a spouse deduction,
so inheritance tax is not applied if the total inheritance amount is up to 160 million yen.
Therefore, only a portion of people will be subject to inheritance tax.
It’s helpful to roughly remember these thresholds.
Just knowing this will make a significant difference when you think about inheritance.
【Inheritance Tax Steps Up After Exceeding the Basic Deduction!】
What happens if the inheritance exceeds the basic deduction?
Inheritance tax will indeed apply,
but it only applies to the portion exceeding the basic deduction.
For example, if the basic deduction is 3,600,000 yen,
and the inheritance is 4,600,000 yen,
then 4,600,000 – 3,600,000 = 1,000,000 yen
will be subject to inheritance tax.
(The source of this information: https://souzoku.asahi.com/article/14937828)
Since 1,000,000 yen exceeds the basic deduction,
the inheritance tax will be 10% on this amount.
A common misconception is that if you inherit 1,100,000 yen,
you might think it falls under the 15% tax zone for amounts below 3,000,000 yen,
but that’s not the case.
Even if you inherit 1,100,000 yen,
the first 1,000,000 yen is taxed at 10%,
1,000,000 × 10% = 100,000 yen.
The remaining 100,000 yen is taxed at 15%,
100,000 × 15% = 15,000 yen.
This tiered approach works just like income tax,
so remember that.
【Inheritance Tax Applies to All of Your Assets!】
What kind of assets does inheritance tax apply to?
The assets that are counted for tax purposes include:
– Cash
– Bank account deposits
– Cars
– Real estate
– Precious metals
…and various other items.
Basically, any asset with monetary value is included.
There are also “deemed inheritance assets,”
which means even life insurance is considered as part of your estate.
However, in the case of life insurance,
only 500,000 yen × the number of legal heirs is exempt from inheritance tax,
so not the full amount is taxable, but it is still considered part of the estate.
Furthermore, overseas assets are subject to inheritance tax.
They will be treated as part of the estate,
with some exceptions, but generally, they are taxable.
Also, be aware of “nominee deposits,”
where the account is under someone else’s name but is actually your money.
For example, if you open an account in your child’s name
to save for them in the future,
even if it’s for inheritance planning,
that money may still be subject to inheritance tax.
So, make sure to keep that in mind.
Special Thanks OpenAI and Perplexity AI, Inc


